Autonomous Weapons Systems (AWS) are military systems capable of selecting and engaging targets without direct human intervention. Here are some key aspects:
- Types of Autonomous Weapons
Drones: Unmanned aerial vehicles that can perform surveillance, reconnaissance, and strike missions.
Robotic Ground Vehicles: Used for bomb disposal, logistics, or combat support.
Naval Systems: Autonomous boats and underwater vehicles for reconnaissance and combat.
- AI Technologies Used
Machine Learning: For target recognition and decision-making.
Computer Vision: To identify and track objects in various environments.
Natural Language Processing: For communication and coordination among systems.

- Advantages
Reduced Risk to Human Life: By taking humans out of immediate danger.
Increased Efficiency: Ability to operate in environments unsuitable for humans.
Speed: Rapid response times in dynamic combat situations.
- Challenges and Concerns
Ethical Implications: Issues around accountability for actions taken by machines.
Escalation of Conflict: The potential for rapid, unintended escalations in warfare.
Reliability and Security: Risks of malfunction or hacking
- Regulation and Oversight
There are ongoing debates within international communities about the need for regulation of AWS to ensure compliance with humanitarian laws and ethical standards.
The conversation around autonomous weapons is complex and involves considerations of technology, ethics, and international security.

United Nations:- The UN Secretary-General has called for a legally binding agreement to prohibit or restrict AWS. The UN also urges states to take action to protect people from the potential threats of AWS
International Committee for Robot Arms Control (ICRAC):- Formed in 2009 and 2010, ICRAC is a global network of scholars working on the topic of AWS.
This global civil society coalition of NGOs was formed by Human Rights Watch to raise awareness of the issue and move it higher on the UN’s arms control agenda.
In May 2024, MPs from over 140 countries approved a resolution calling for parliaments to discuss and regulate AWS.
Examples of autonomous weapons include:
Mines
Land mines have been used since the 1600s, and naval mines have been used since the 1700s.
Missile defense systems
These systems can autonomously detect and engage targets, and issue warnings. Examples include Iron Dome.
Sentry systems
These systems can autonomously detect and engage targets, and issue warnings. Examples include stationary sentry guns used in South Korea and Israel.
Loitering munitions
Also known as suicide, kamikaze, or exploding drones, these systems contain a built-in warhead and wait around a predefined area until a target is located.
Drones
Drones can be used for surveillance and targeted strikes. For example, the MQ-9 Reaper drone can carry out autonomous flight.
Uncrewed combat vehicles
These vehicles can be designed to attack from ambush. For example, the Jaeger-C has two modes of operation: Chariot mode and Goliath mode.
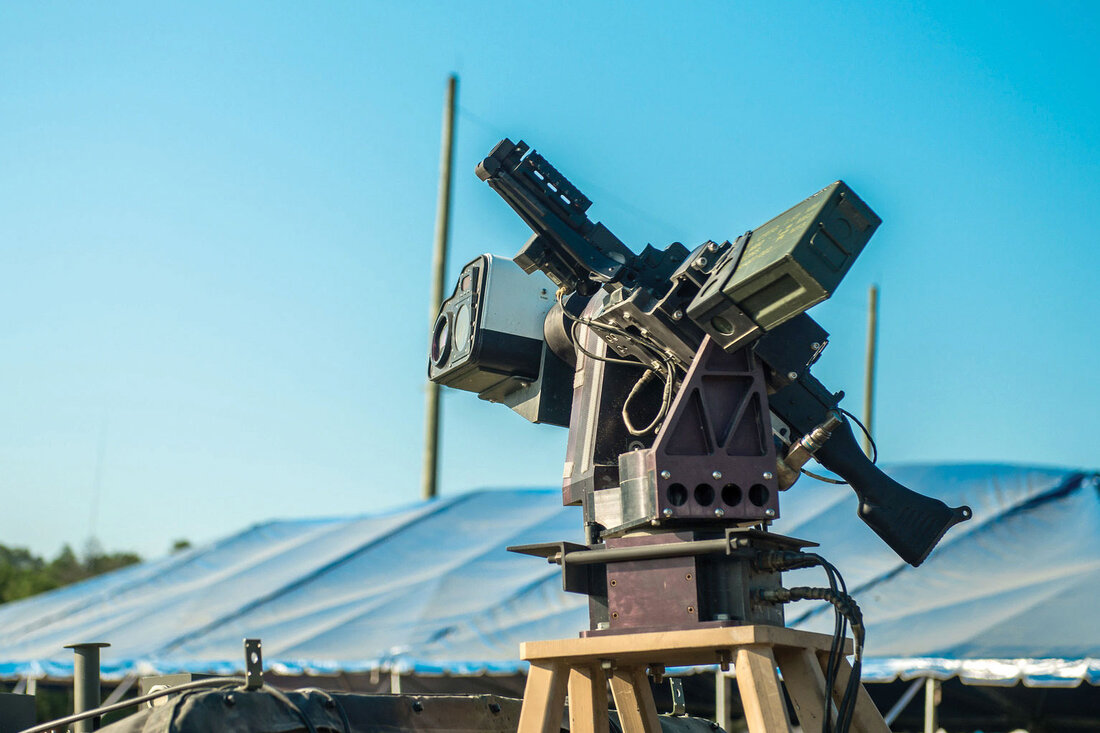
Active protection systems
These systems can autonomously identify and attack oncoming missiles, rockets, artillery fire, aircraft, and surface vessels. For example, the US Phalanx CIWS.
 Many countries, including China, Israel, Russia, South Korea, Türkiye, the United Kingdom, and the United States, are reported to be investing in building autonomous weapons.
Many countries, including China, Israel, Russia, South Korea, Türkiye, the United Kingdom, and the United States, are reported to be investing in building autonomous weapons.
